Box sets » Welfare spending » State pension
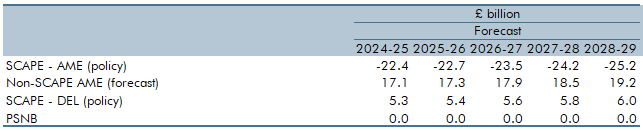
The new SCAPE discount rate, to be implemented in April 2024, increases the present value of future pensions payments and in turn causes employer contributions to rise. Box 4.4 explained the SCAPE rate change and its overall impact on the public finances.
The Government commissioned two reports published in 2017 to inform its review of the State Pension age (SPA): an independent review by John Cridland and a report by the Government Actuary’s Department (GAD). This box summarised the key findings from these two reports.
Our 2018 long-term fiscal projections suggested that, if left unaddressed, the public sector finances would come under increasing pressure over the next 50 years. This box compared our long-term age related spending projections over the period from 2025 to 2065 with those presented in the European Commission's 2018 Ageing Report.
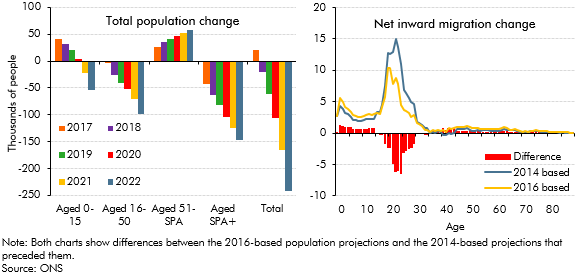
The Office for National Statistics (ONS) published new UK population projections in October 2017, based on 2016 population estimates and updated assumptions for fertility, mortality and net migration. This box compared the latest projections with the previous 2014-based principal projections that underpinned our March 2017 forecast and summarised their effects on our November 2017 fiscal forecast.
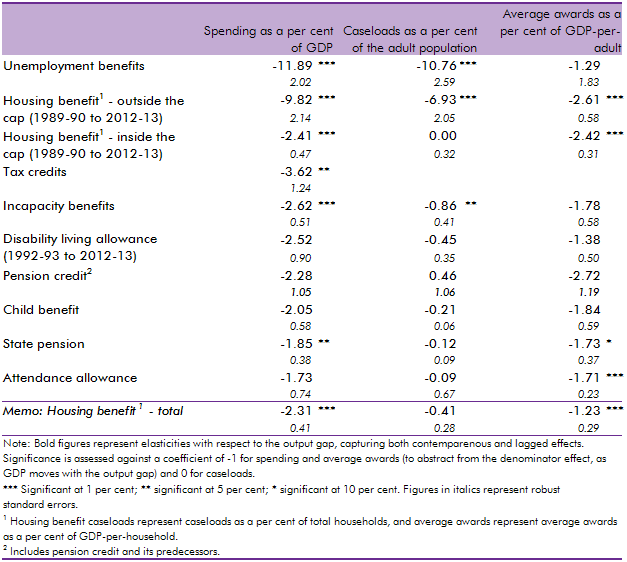
In our 2014 Welfare trends report, Chapter 4 reviewed the overall trends in welfare spending. In this box, we considered how responsive welfare spending is to the economic cycle by estimating the elasticity of benefits and tax credits spending as a share of GDP with respect to changes in the output gap (the difference between actual GDP and an estimate of its potential or underlying level). We found that the most counter-cyclical benefits have caseloads closely associated with the economic cycle whereas mildly counter-cyclical benefits are likely to only exhibit cyclicality due to spending varying less than GDP, thereby producing a denominator effect.
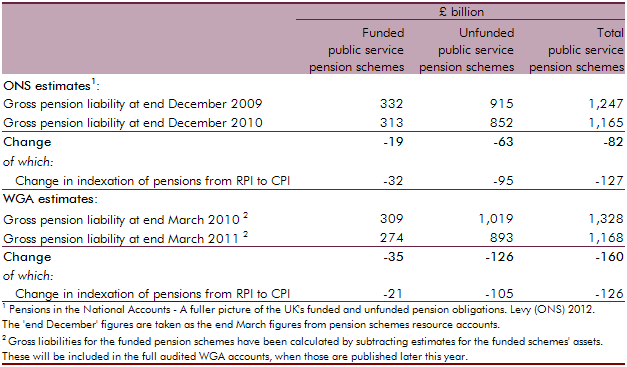
In April 2012, the Office for National Statistics (ONS) published the first set of new statistics on the total gross liabilities of UK pension providers, including the UK government. This box explored how the ONS’ pension liability estimates were calculated for public service pensions and state pensions, and compared the public service estimate to the Whole of Government Accounts (WGA) methodology.
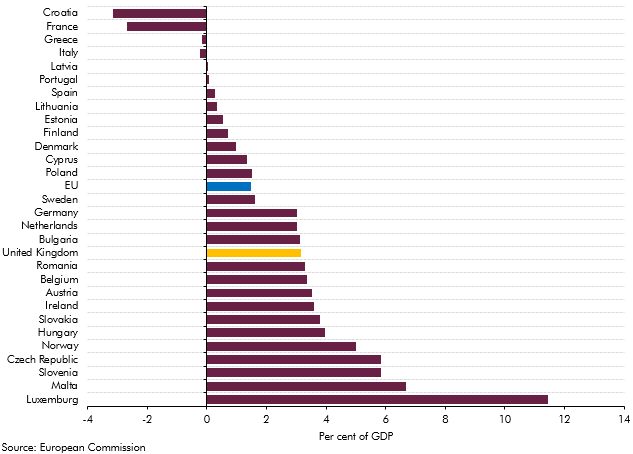
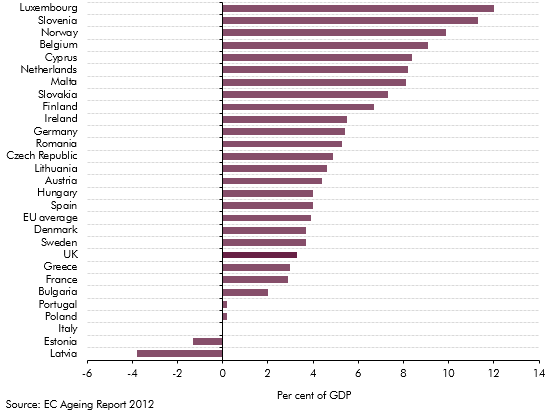
The European Commission (EC) produces its own analysis of ageing pressures for member states every three years. This box contrasted the forecast made by the EC and the OBR for UK age related spending such as pensions, health care and long-term care.
This box set out the various impacts that higher inflation has on the public finances. These include direct effects (e.g. on income tax and debt interest spending), the impact on nominal tax bases (such as household consumption) and the impact on departmental spending.