Box sets » Economic and fiscal outlook - March 2017
All elements of GDP data are subject to revision, which creates one source of uncertainty in our forecasts. Business investment data are particularly prone to revision. In this box from our March 2017 Economic and fiscal outlook we looked at past revisions in business investment data and compared the volatility and average revision of UK data with those produced by other countries.
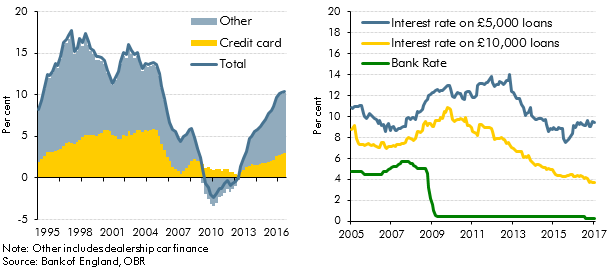
Strong growth in consumer credit in the run-up to our March 2017 Economic and fiscal outlook had prompted concerns among some commentators about its sustainability. In this box we considered the drivers of consumer credit growth, including the role of dealership car finance, and the extent to which it may have supported household consumption growth.
In each Economic and fiscal outlook we publish a box that summarises the effects of the Government’s new policy measures on our economy forecast. These include the overall effect of the package of measures and any specific effects of individual measures that we deem to be sufficiently material to have wider indirect effects on the economy. In our March 2017 Economic and Fiscal Outlook, we adjusted our economy forecast for the effects of reducing the ‘personal injury discount rate’.
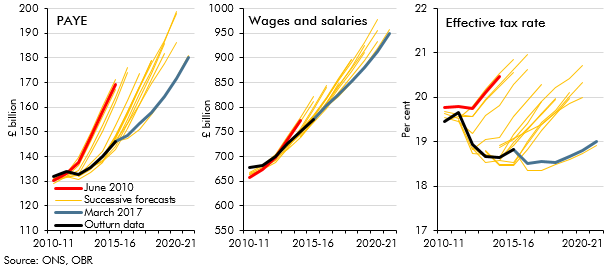
PAYE income tax is the Government’s single most important source of revenue, and one where our forecasts since 2010 have tended to be revised down over time. In this box from our March 2017 Economic and fiscal outlook, we explored the role that changes in the distribution of earnings might have played in explaining the shortfalls in income tax receipts.
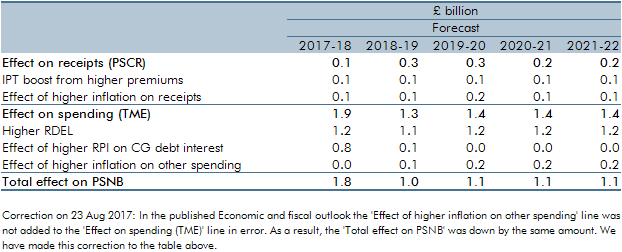
In February 2017, just ahead of the Spring Budget and our March Economic and fiscal outlook, the Ministry of Justice announced that the ‘personal injury discount rate’ would be reduced from 2.5 to minus 0.75 per cent (in inflation-adjusted real terms). This box explained the direct and indirect effects of this change on our receipts and public spending forecasts.
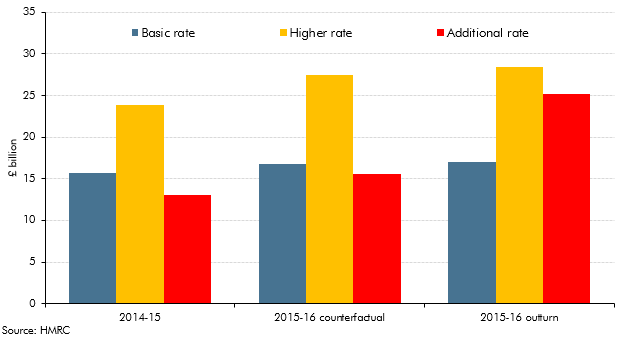
Ahead of our March 2017 Economic and fiscal outlook, self-assessment tax receipts indicated that the Summer Budget 2015 reforms to the taxation of individual dividend income had prompted even greater income shifting than we had expected. The reforms raised the basic, higher and additional rates by 7.5 percentage points from April 2016 and introduced a tax-free allowance on the first £5,000 of taxable annual dividend income. They were pre-announced, giving taxpayers around eight months to bring forward dividend income into 2015-16 so that it was taxed at the lower rate. This box considered the amount of income brought forward and the effect of that on tax receipts.
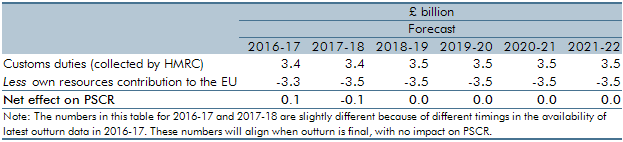
Our post-EU referendum publications noted many direct or indirect Brexit-related uncertainties across our economy and fiscal forecasts. One area that will be directly affected after Brexit is customs duties. In our March 2017 Economic and fiscal outlook, this box outlined the how customs duty was currently treated in the public finances data and the fiscally neutral approach that we had used in our forecast pending further information on post-Brexit policy settings.
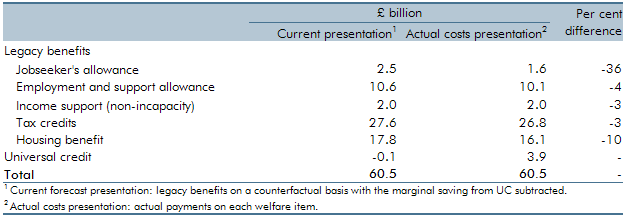
A key issue in our welfare spending forecast is the transition to universal credit (UC) from the existing ‘legacy’ benefits and tax credits systems. In our March 2017 Economic and fiscal outlook, our central forecast was constructed by forecasting the ‘legacy’ system as though UC did not exist, then subtracting from it an estimate of the marginal saving associated with rolling out UC. This box presented estimates for actual gross spending in 2017-18 on UC and the legacy benefits and tax credits that it is replacing.
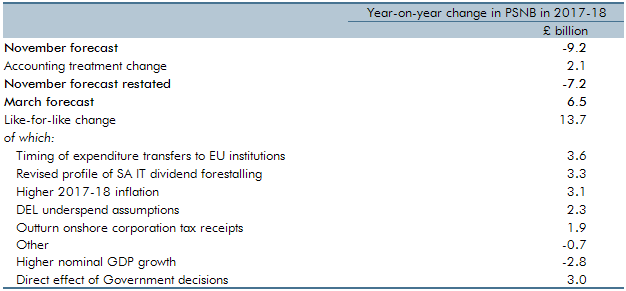
For the first time in any Economic and fiscal outlook, our March 2017 forecast showed post-measures borrowing rising year-on-year in one year of the forecast – 2017-18. This box explored the factors that explained why borrowing was expected to rise in that year, when our November 2016 forecast had assumed it would continue to fall.