Box sets » Welfare spending » Unemployment benefits
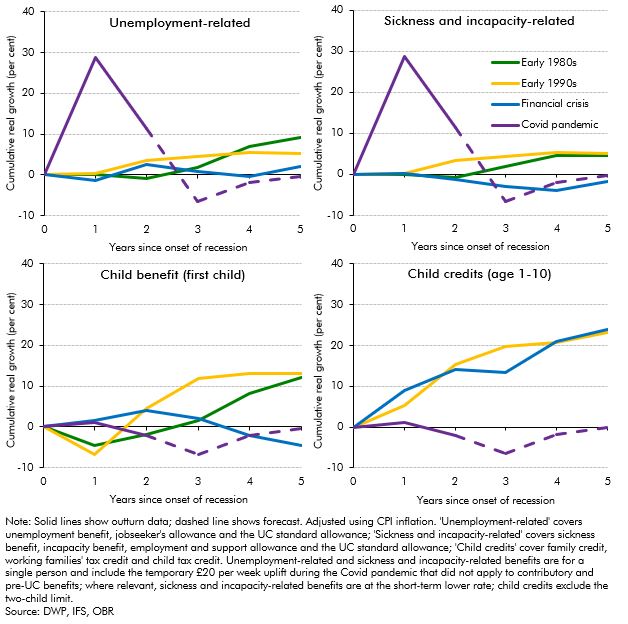
The real-terms value of benefits was forecast to fall by around 5 per cent in 2022-23 (£12 billion in total) before catching up the year after, largely due to the significant rise in inflation and the lag in benefit uprating. In this box we compared these post-pandemic uprating dynamics to the real value of non-pensioner benefit rates following the previous three recessions. This showed that the forecast trough in the real value of benefits was deeper in the wake of the pandemic than for any of the previous three recessions.
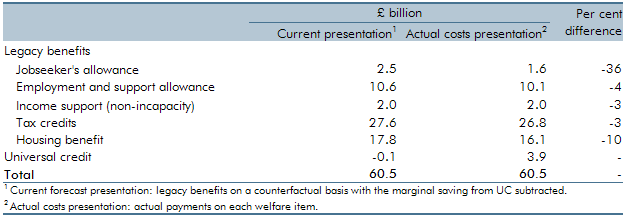
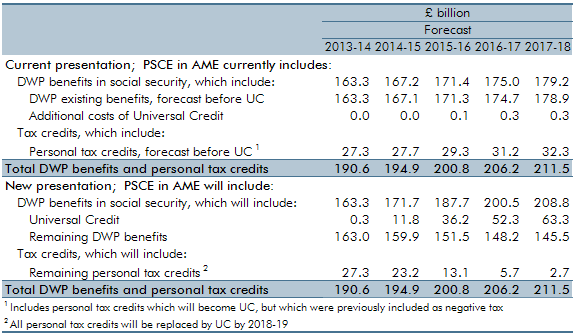
A key issue in our welfare spending forecast is the transition to universal credit (UC) from the existing ‘legacy’ benefits and tax credits systems. In our March 2017 Economic and fiscal outlook, our central forecast was constructed by forecasting the ‘legacy’ system as though UC did not exist, then subtracting from it an estimate of the marginal saving associated with rolling out UC. This box presented estimates for actual gross spending in 2017-18 on UC and the legacy benefits and tax credits that it is replacing.
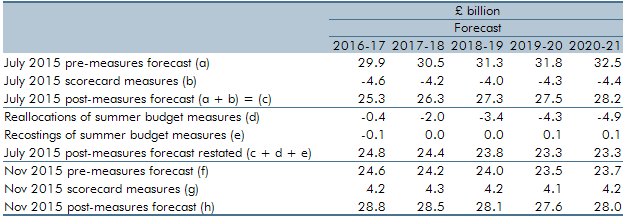
The July 2015 Budget included a large number of complex welfare measures that cut across multiple benefits with many interactions. At Autumn Statement 2015, we identified a number of measures where interaction effects had not been correctly estimated or classified. In this box of our November 2015 EFO, we discussed the re-estimation and reclassification of the interaction effects of a number of welfare measures. This included the reclassification of three tax credits measures and the measure extending the `lone parent obligation’ to ensure that these costings were consistent with our marginal universal credit (UC) forecast. The impact of cuts to tax credits on housing benefit entitlement were also re-estimated and reallocated to the housing benefit forecast from the tax credits forecast as the effect had previously been incorrectly allocated to tax credits.
In Chapter 4 of our December 2014 EFO, we discussed the fiscal outlook for 2014-15 to 2018-19. In this box, we discussed the latest universal credit rollout plan following the 2014 universal credit business case. Whilst we agreed that the plan to fully rollout universal credit for jobseeker’s allowance cases by March 2016 was central, we decided that the migration plan for claimants of other legacy benefits was still highly uncertain and so implemented a six month delay to the plans for our forecast. This had the effect of reducing the volume of migrations in all years of the forecast but did not substantially alter the universal forecast given that it marginal to the legacy benefits.
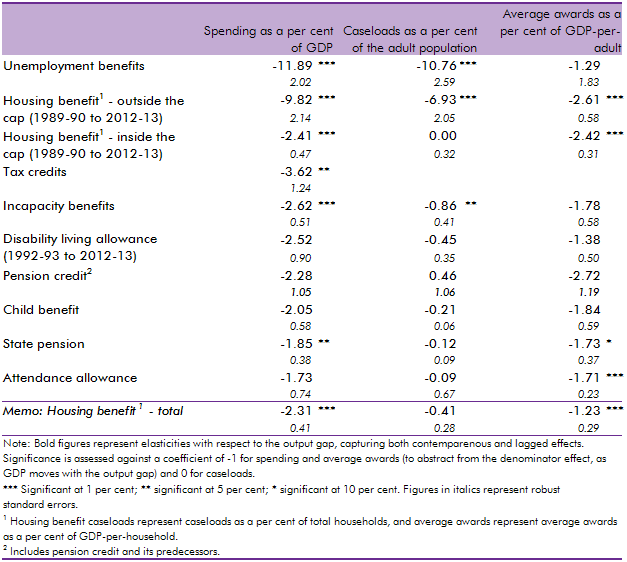
In our 2014 Welfare trends report, Chapter 4 reviewed the overall trends in welfare spending. In this box, we considered how responsive welfare spending is to the economic cycle by estimating the elasticity of benefits and tax credits spending as a share of GDP with respect to changes in the output gap (the difference between actual GDP and an estimate of its potential or underlying level). We found that the most counter-cyclical benefits have caseloads closely associated with the economic cycle whereas mildly counter-cyclical benefits are likely to only exhibit cyclicality due to spending varying less than GDP, thereby producing a denominator effect.
In our 2014 Welfare trends report, Chapter 4 reviewed the overall trends in welfare spending. In this box we discussed the latest Universal Credit (UC) forecast at the time of writing. This forecast assumed UC would roll-out slowly during 2014-15 and 2015-16 before accelerating in 2016-17 and 2017-18, by which time 5.8 million people were expected to be receiving the benefit. We highlighted that the roll out of UC had already been subject to previous delays and that the decision to produce a top-down UC forecast helped mitigate the uncertainties caused by delivery challenges. We then decomposed the marginal UC forecast into its constituent gross savings and gross costs forecasts.
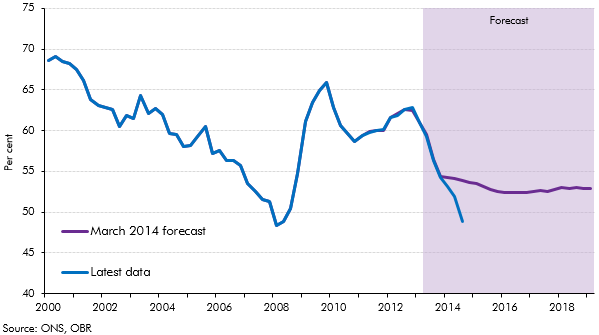
In our 2014 Welfare trends report, Chapter 8 considered spending on unemployed people. This box compared outturn data on unemployment and claimants of unemployment benefits to the levels implied by our March 2014 forecast. As the economy performed better than anticipated in our March 2014 forecast, the ratio of claimants of unemployed benefits to the Labour Force Survey (LFS) measure of unemployment deviated from our projections. This was largely due to a drop in the rate of inflows into unemployment benefits and a rise in the rate of outflows from unemployment benefits, though an increase in the number of people looking for jobs but not claiming unemployment benefits may have increased LFS unemployment and so been a contributing factor.
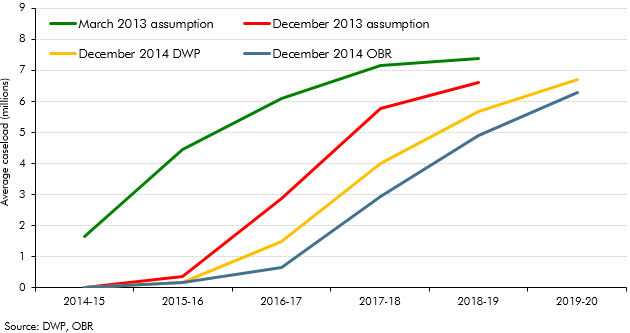
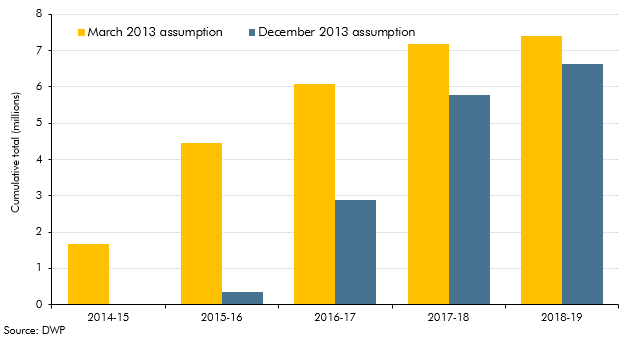
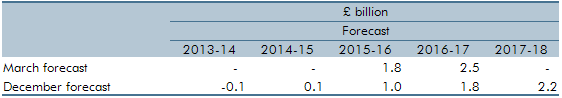
In Chapter 4 of our December 2013 EFO, we discussed the fiscal outlook for 2013-14 to 2017-18. In this box, we discussed the delays to the Government’s universal credit rollout plan. Compared to the March 2013 rollout plan, large increases in the universal credit caseload were assumed to start later than previously planned in 2016 and 2017. Fewer people were also expected to be on universal credit at the end of the forecast horizon, with 700,000 fewer claimants assumed to have migrated by the end of 2017-18 compared to the March 2013 rollout plan. We explained that the changes to the rollout schedule was a key source of change in the profile of our forecast relative to March 2013, with lower spending up to 2015-16.
In Chapter 4 of our March 2013 EFO, we discussed the fiscal outlook for 2013-14 to 2017-18. In this box, we introduced a new marginal cost presentation of the universal credit forecast and also outlined contributing factors to changes in the forecast. These factors included policies announced at the 2012 Autumn Statement and changes to a number of the universal credit policy parameters as well as refinements to the methodology and assumptions used to forecast universal credit. The analysis in this box has since been superseded by developments in the universal credit forecast.
In Chapter 4 of our December 2012 EFO, we discussed the fiscal outlook for 2012-13 to 2016-17. In this box, we discussed changes to the provisional universal credit forecast that was included in our March 2012 EFO. Changes to the forecast were due to a number of factors, including policies announced at Budget 2012 and finalisation of policy parameters in universal credit as well as .refinements to the methodology and assumptions used to forecast universal credit. We also discussed the main uncertainties in the forecast, which largely related to the unpredictability given the scale of the policy. The analysis in this box has since been superseded by developments in the universal credit forecast, though many of the key uncertainties remain.