Box sets » Primary balance
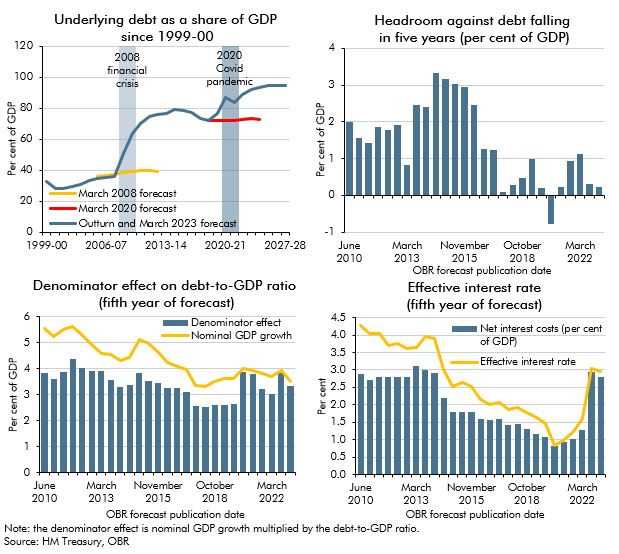
Public sector net debt (ex BoE) has risen substantially over the past 25 years, despite repeated government plans to get it falling. In this box, we examined the key drivers behind this upward trend, including the impact of major economic shocks, the persistent gap between forecasted and actual debt outcomes, and the increasing difficulty of stabilising debt due to structural fiscal pressures.
Since the financial crisis successive Chancellors have aimed to reduce debt as a share of GDP. This box looked at why that goal had proved difficult to achieve and in particular the challenges in our most recent forecasts.
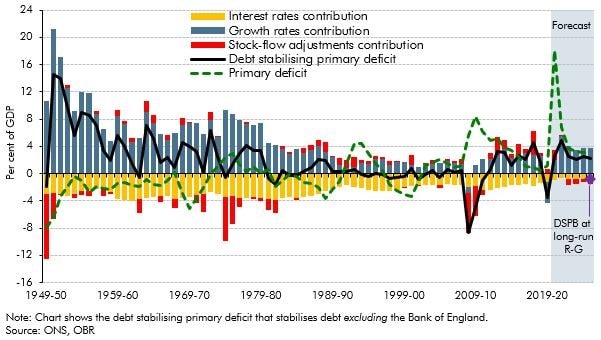
The debt-stabilising primary deficit depends on the level of debt, nominal growth rates, the effective nominal interest rate, and any 'stock-flow adjustments'. This box discussed the historical evolution of the debt stabilising primary balance, and also explained why it may appear to be ‘easier’ to stabilise debt the higher it rises, and the fiscal risks that such an interpretation entails.
In our 2015 Fiscal sustainability report, we assumed that GDP grows in line with its historical trend. This in effect implied 47 years of uninterrupted trend economic growth in our central projections. This box considered the alternative paths for debt as a share of GDP under an symmetric and asymmetric cycle, highlighting the sensitivity of the net debt projections to economic cycles.
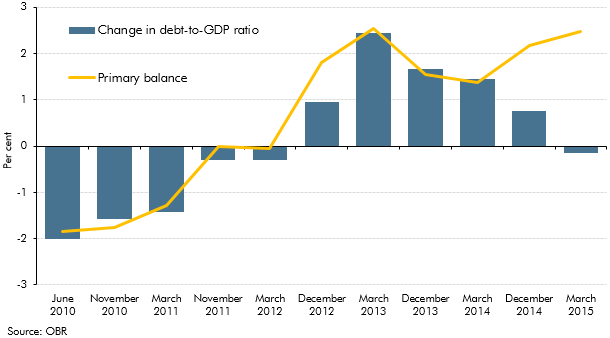
In our first June 2010 EFO, the debt-to-GDP ratio was forecast to fall by 2 per cent in 2015-16. This box explored how our debt-to-GDP forecast for 2015-16 evolved over time. It highlighted the contribution of the primary balance and the impact of other factors (including asset sales and the growth-interest differential) on the debt-to-GDP ratio forecast.