Box sets » Labour market » National Minimum Wage and National Living Wage
In March 2020, the Government introduced a new target for the National Living Wage (NLW) to reach two-thirds of median earnings (of the relevant population) by 2024, providing economic conditions allow. In this box we considered the effect of this policy change on the outlook for the economy and the public finances.
Alongside the October 2018 Economic and fiscal outlook (EFO) the Government expressed its aspiration to end low pay, noting the definition used by the OECD, which corresponds to two-thirds of median earnings. This policy was not firm enough for us to incorporate into our central forecast. Nevertheless, in this box we drew on previous analysis from our July 2015 EFO – when the National Living Wage was first introduced – to illustrate the potential effect on the economy and public finances.
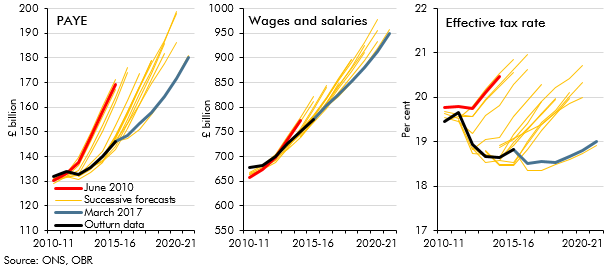
PAYE income tax is the Government’s single most important source of revenue, and one where our forecasts since 2010 have tended to be revised down over time. In this box from our March 2017 Economic and fiscal outlook, we explored the role that changes in the distribution of earnings might have played in explaining the shortfalls in income tax receipts.
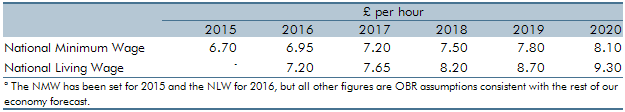
In July 2015, the Government announced the ‘National Living Wage’ (NLW) for workers aged 25 and above. This box from our November 2015 Economic and fiscal outlook outlined how revisions to the wider economy forecast affected our NLW forecast and also explored some of the potential labour market and employer responses to the NLW.
In each Economic and fiscal outlook we publish a box that summarises the effects of the Government’s new policy measures on our economy forecast. These include the overall effect of the package of measures and any specific effects of individual measures that we deem to be sufficiently material to have wider indirect effects on the economy. In the July 2015 Economic and fiscal outlook, we made a number of adjustments to real and nominal GDP, the labour market, inflation, business and residential investment, and the housing market.