Box sets » Receipts » Business rates
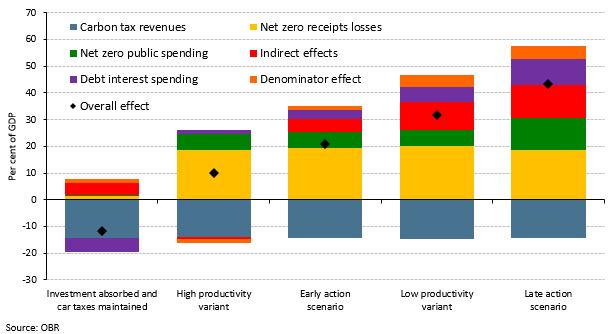
Our 2021 Fiscal risks report explored the fiscal risks posed by climate change and the Government’s commitment to reduce the UK’s net carbon emissions to zero by 2050. This box examined the policies announced in the Budget, Spending Review, and Net Zero Strategy in October 2021, and the significant rises in market prices for hydrocarbons since we completed our Fiscal risks report, and how they had changed the risks associated with climate change and decarbonisation.
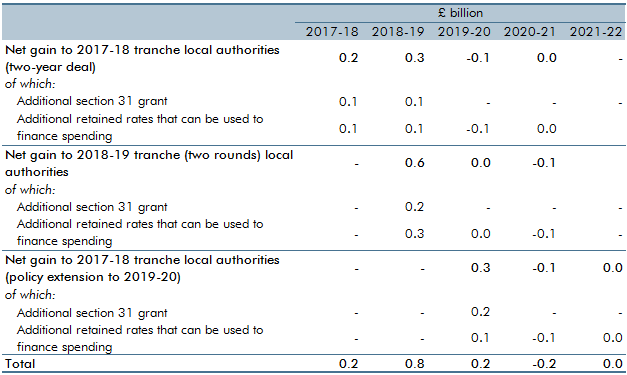
The Government has been piloting full business rates retention since 2017-18. These pilots featured in our forecasts from March 2017. This box reconsidered and re-estimated the fiscal effects of the 100 per cent local retention pilots scheme.
Business rates are a major source of locally-raised finance used to fund locally-administered spending. The Government announced in Autumn Statement 2015 that it would let English local authorities retain 100 per cent of business rates by the end of the Parliament. This box outlined the change in local government financing arrangements and the responsibilities that might be devolved, as well as how these changes would affect our forecast.
In this forecast, there were two policy switches that shifted spending between RDEL and AME, which applied from 2015-16 onwards. This box outlined these changes and examined the subsequent impact these would have on our forecast.
‘Computable general equilibrium’ (CGE) modelling is a tool for assessing the potential medium and long-term economic impact of policy changes. This box explored recent Government CGE studies of cuts to corporation tax and fuel duties alongside the potential impact of other recent tax rises and spending cuts.
This box set out the various impacts that higher inflation has on the public finances. These include direct effects (e.g. on income tax and debt interest spending), the impact on nominal tax bases (such as household consumption) and the impact on departmental spending.